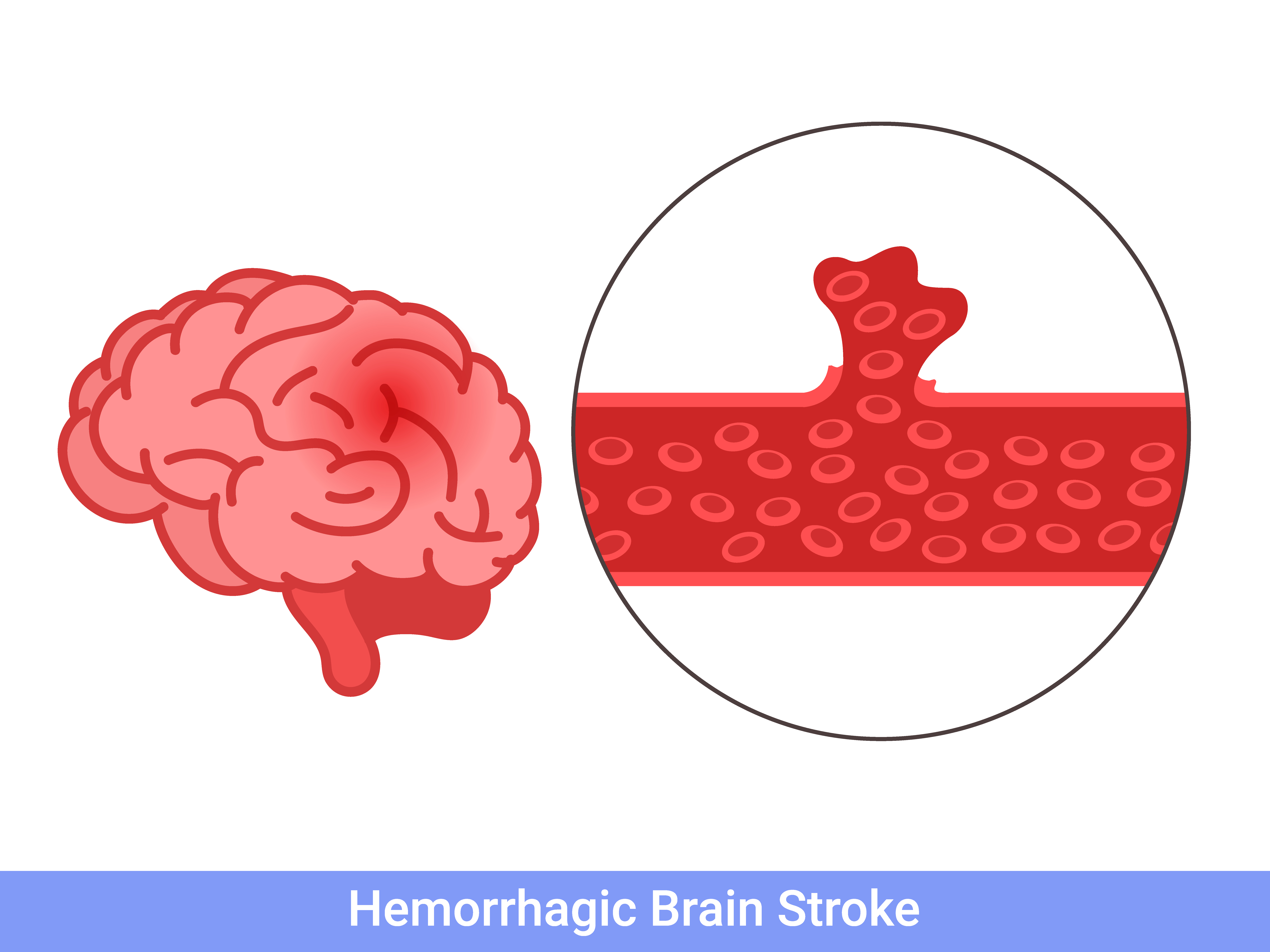
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures and bleeds into the brain. Unlike ischemic strokes, which are caused by clots, a hemorrhagic stroke is a medical emergency involving a brain bleed. Immediate action is critical to limit brain damage and increase the chance of survival. According to Dr. Vivek Gupta, recognizing the signs early and responding promptly can significantly improve outcomes.
Knowing what to do during a hemorrhagic stroke can make all the difference. Let’s walk through the essential steps of emergency response.
Recognizing a Hemorrhagic Stroke
The symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke can come on suddenly and be severe. Common signs include:
- Sudden, severe headache
- Loss of consciousness or confusion
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision problems
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Nausea or vomiting
If you observe these signs, treat it as a stroke emergency and act fast.
First Aid for Hemorrhagic Stroke
Here’s what to do in a hemorrhagic stroke emergency before medical help arrives:
- Call Emergency Services Immediately
Dial emergency medical services. Time is crucial. Early medical intervention can reduce brain damage.
- Keep the Person Still and Calm
Prevent unnecessary movement. Let them lie down with their head slightly elevated. Avoid giving them food, drink, or medication unless directed by professionals.
- Monitor Their Breathing
If the person becomes unconscious, check for breathing. If they are not breathing or have no pulse, begin CPR if you’re trained.
- Note the Time Symptoms Began
Medical professionals need to know how long the symptoms have been present. This will help guide treatment decisions.
- Avoid Panic
Stay calm. Reassure the person if they’re conscious. Panic can worsen the situation for both you and the patient.
Why Quick Action Matters
A brain hemorrhage causes pressure and swelling that can rapidly damage brain tissue. Immediate medical care, which may include surgery or blood pressure management, is often needed to stabilize the patient. The faster you respond, the better the outcomes.
After the Emergency
Even after hospital care, patients often require stroke rehabilitation, which may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy to regain lost functions. Families also need guidance on how to support recovery at home.
For expert stroke care and emergency guidance, consult us!

Comments 0