Every September, worldwide, we observe Brain Aneurysm Awareness Month — a time dedicated to educating people about a condition that is often silent until it becomes life-threatening.
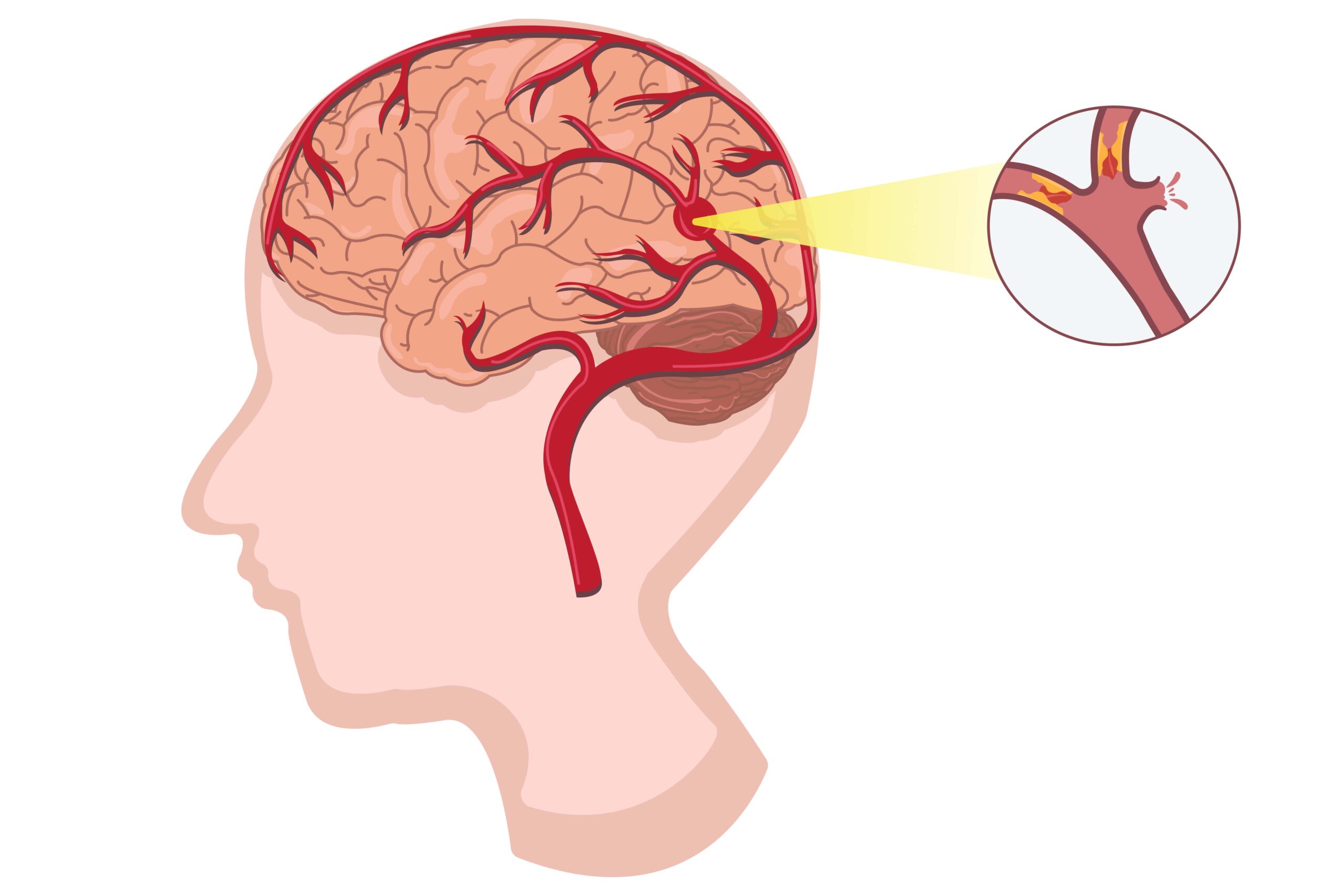
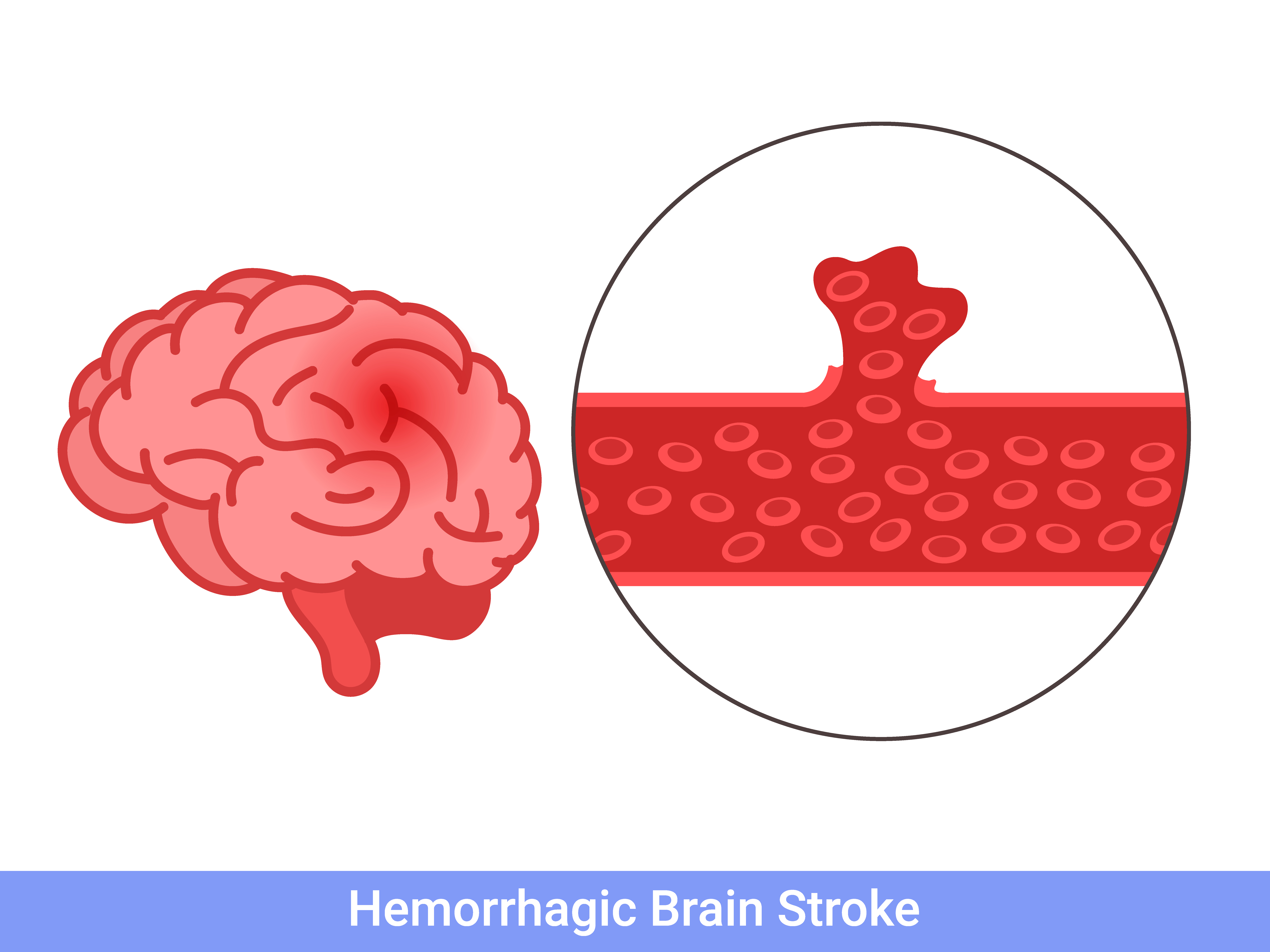
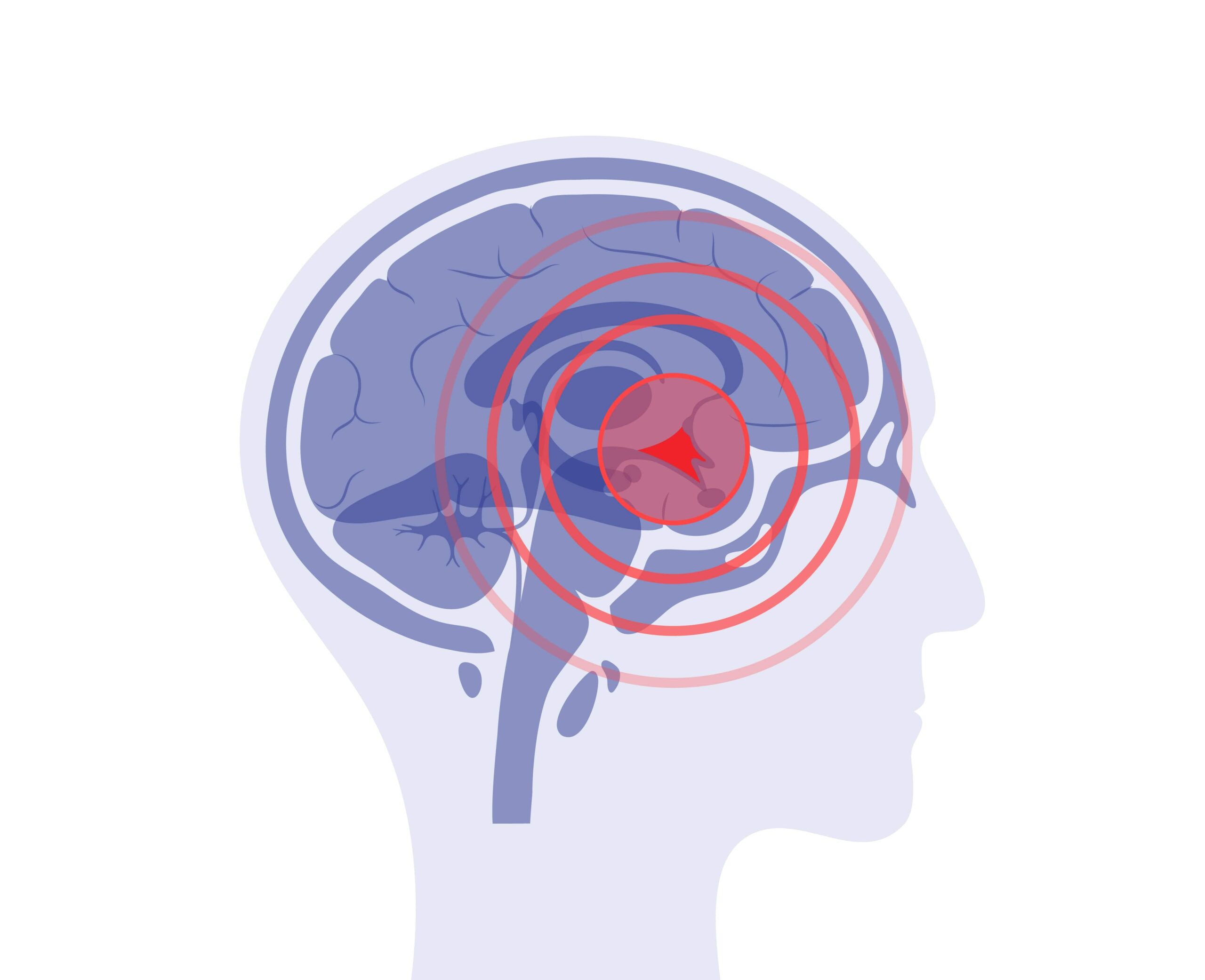
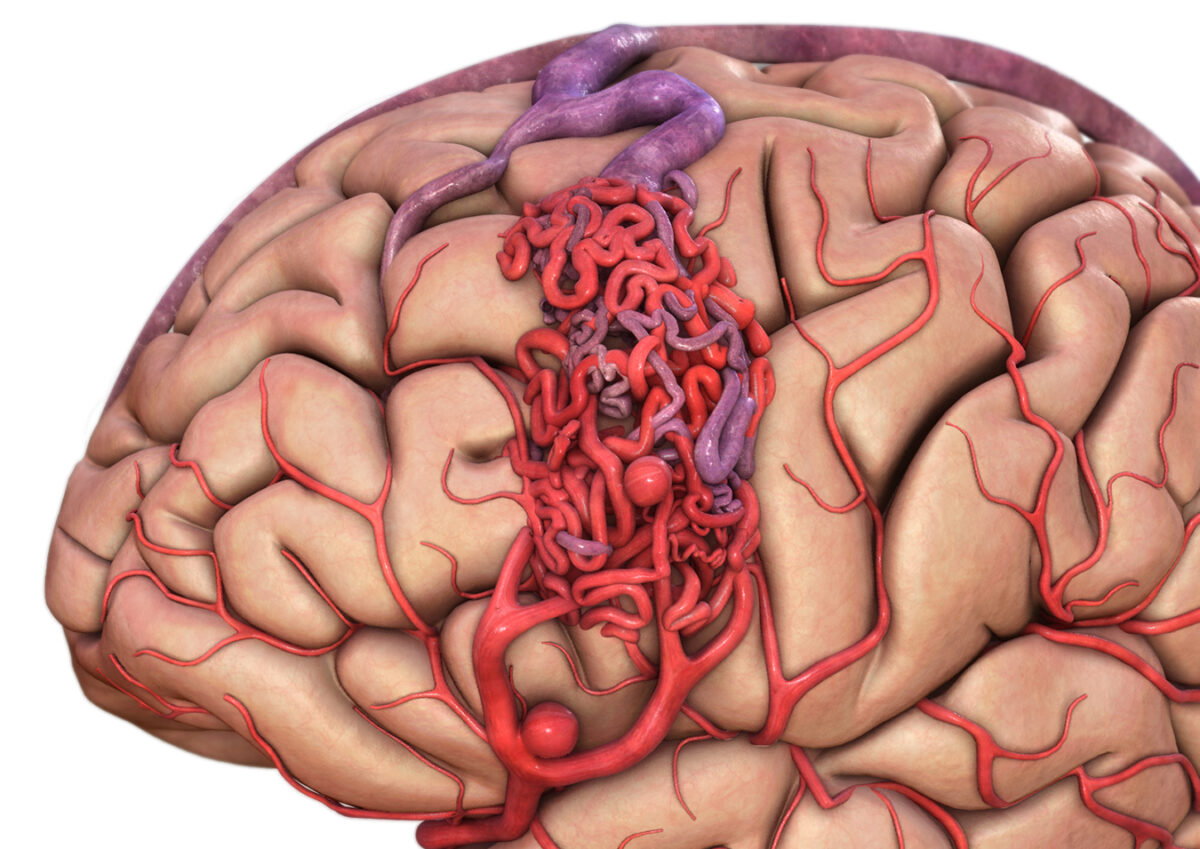
A brain aneurysm occurs when a blood vessel in the brain develops a weak area in its wall, causing it to bulge. You can think of it like a small balloon or blister on the side of the vessel. In some cases, these aneurysms remain stable and never cause symptoms. But in others, the bulge can rupture, leading to bleeding in the brain — a medical emergency known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
The challenge? Brain aneurysms can exist for years without warning signs. And yet, when they rupture, they can be deadly within minutes. This is why awareness is crucial — because when it comes to aneurysms, early detection and rapid action save lives.
The Numbers You Should Know
- 1 in 50 people has an unruptured brain aneurysm (found in a study done in the US).
- Each year, around 500,000 people worldwide die from brain aneurysms or their complications.
- 50% of ruptures are fatal, and among survivors, about two-thirds suffer long-term neurological deficits.
- Brain aneurysms are most common between the ages of 35 and 60, but they can occur at any age.
- Women are more likely to develop aneurysms than men, by about a 3:2 ratio.
These are not just numbers — they represent friends, family members, and colleagues whose lives can change in an instant.
How a Brain Aneurysm Can Hide in Plain Sight
One of the most dangerous things about brain aneurysms is how they often blend into daily life. In my practice, I’ve seen patients who had subtle symptoms weeks or months before a rupture — symptoms that were mistaken for stress, fatigue, or eye strain.
Common Warning Signs (Before Rupture)
- Persistent headaches, often localized behind the eyes or at the back of the head.
- Vision changes — blurred vision, double vision, or trouble focusing.
- Neck pain or stiffness that doesn’t improve.
- Drooping eyelid or changes in pupil size.
- Tingling or weakness on one side of the face or body.
These signs may not always mean you have a brain aneurysm, but they should never be ignored, especially if they are new, sudden, or severe.


The “Thunderclap” — When a Rupture Happens
When a brain aneurysm bursts, it’s often described as the worst headache of your life — sudden, intense, and unlike anything you’ve ever felt. Other symptoms of rupture include:
- Sudden nausea and vomiting
- Loss of consciousness (even for a brief moment)
- Seizures
- Trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden confusion or disorientation
In these moments, every second counts. Immediate medical attention can mean the difference between survival and fatality.
Everyday Factors That Raise the Risk
It’s easy to think of brain aneurysms as rare events that “happen to other people.” But the truth is, everyday lifestyle choices and health conditions can quietly increase your risk:
- High blood pressure — often from stress, poor diet, or lack of exercise.
- Smoking, which weakens blood vessel walls.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Drug abuse, particularly cocaine or amphetamines.
- Family history — a close relative with a brain aneurysm increases your own risk.
Even something as simple as ignoring regular health check-ups can allow silent risks to go unnoticed.
Relatable Scenarios — Why Awareness Matters
Imagine you are at work, and you feel a sudden, severe headache accompanied by blurred vision. You tell yourself, “I’ve been staring at the computer too long.” Or maybe you wake up with neck stiffness and chalk it up to a bad pillow.
In many cases I’ve treated, these small, everyday moments were early warning signs — but by the time the patient sought help, the aneurysm had ruptured.
The takeaway? Don’t ignore your body’s alarms. It’s better to get checked and find nothing than to wait until it’s too late.
Early Detection is Possible
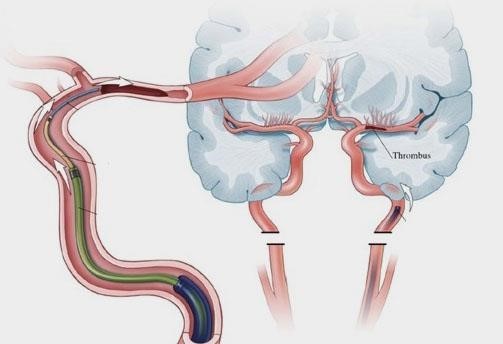
The good news is that modern imaging techniques like MRI, CT angiography, and digital subtraction angiography can detect aneurysms before they rupture.
At Fortis Hospital, Mohali, our Neurointerventional Neuroradiology team uses advanced imaging and minimally invasive procedures like:
- Endovascular coiling — sealing off the aneurysm from the inside.
- Surgical clipping — placing a clip at the base to stop blood flow into it.
Both treatments are highly effective when the aneurysm is caught in time.
How You Can Protect Yourself
- Know your family history — If a parent or sibling had an aneurysm, discuss screening with your doctor.
- Manage your blood pressure — through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Quit smoking — this is one of the most important steps you can take for vascular health.
- Limit alcohol — excessive drinking increases your risk.
- Don’t ignore symptoms — even if they seem small.
- Schedule regular check-ups — prevention starts with knowing your numbers (BP, cholesterol, sugar levels).
Brain aneurysms may be silent, but awareness can give them a voice before it’s too late. Share this knowledge with your friends and family — it could save a life.
If you have concerns or a family history of brain aneurysms, consult us for screening, diagnosis, and treatment.